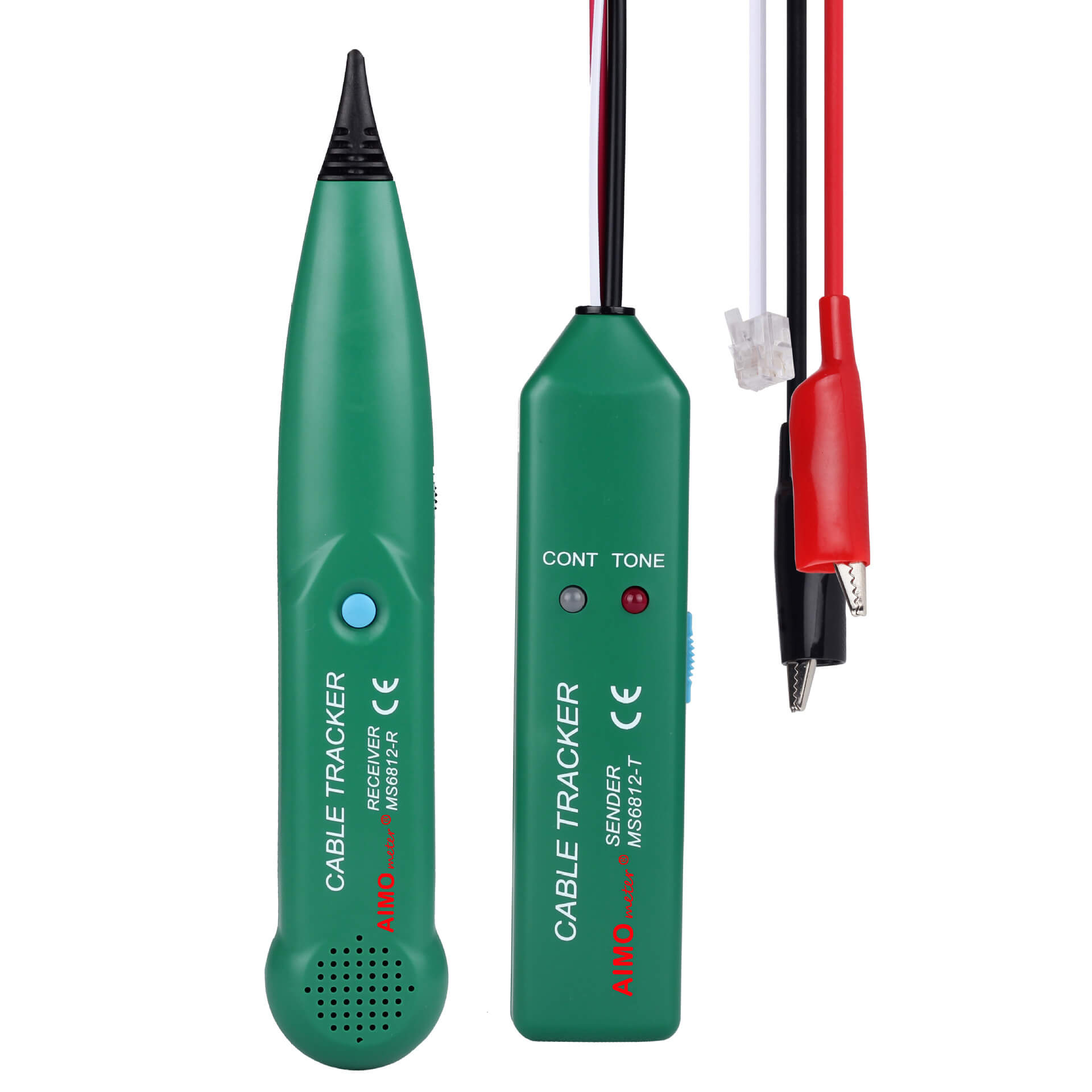
High-temperature wire is commonly used in environments that are subject to high temperatures and harsh conditions. Some common examples include motor leads, internal wiring in appliances, heat pumps, clothes dryers, and refrigeration equipment. These wires can also be used in chemical and glass plants. These wires can withstand temperatures up to 125 degrees Celsius.
UL Recognized Components for high-temperature wire
High-temperature wire has many uses in harsh and elevated environments. Some of these applications include motor leads, heat pumps, clothes dryers, and the internal wiring of appliances. Other uses include industrial and commercial ovens and glass and chemical plants. These wires are commonly found in a wide variety of industries, and they are UL-certified to withstand extreme temperatures.
When choosing a high-temperature wire, consider the ampacity and temperature range. The temperature rating is the highest continuous temperature the wire can withstand, while the ampacity is the highest current the insulated conductor can safely carry without exceeding its jacket and insulation temperatures. While temperature ratings are important, you should also consider the cost.
The temperature rating and ampacity are two important factors in choosing high-temperature wire. The temperature rating is the maximum temperature that a wire can safely withstand over a long period of time. Ampacity refers to the maximum current that an insulated conductor can safely carry without exceeding the limits of its jacket or insulation. There are also several flammability considerations to consider.

 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 简体中文
简体中文 GERMAN
GERMAN SPAIN
SPAIN
 +86 181-5747-1135
+86 181-5747-1135






 Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135
Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135 FAX: +86 574 8900 7636
FAX: +86 574 8900 7636 E-mail:
E-mail: 

 read the map
read the map