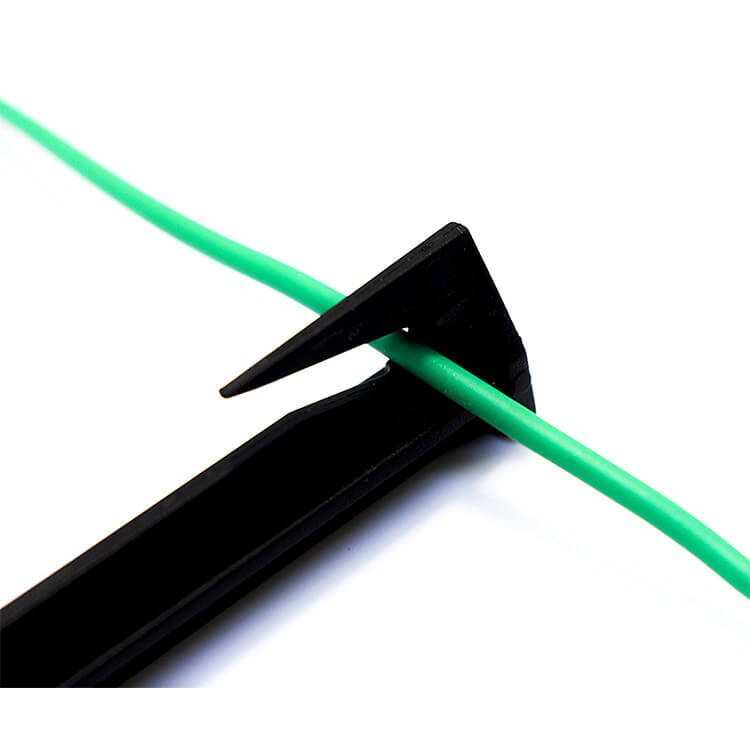
Automotive wire is different from ordinary household cables. Ordinary household wires are copper single-core wires with a certain degree of hardness. The automotive wires are all copper multi-core flexible wires. Several or even dozens of flexible copper wires are wrapped in a plastic insulating tube (PVC), which is soft and not easy to break. Due to the particularity of the automobile industry, the manufacturing process of the automobile wire is also more special than other ordinary wires.

There are two types of automotive wires: high-voltage wires and low-voltage wires, both of which are processed with copper multi-core flexible wires. The cross-sectional area of the wire is mainly selected according to its working current. For electrical appliances that produce very small currents, in order to ensure that the wires should have a certain mechanical strength, the cross-sectional area of the wires should not be less than 0.5mm2. Since the starter works for a short period of time, in order to ensure that the starter can emit sufficient power during normal operation, it is required that the voltage drop generated by each 100A current on the line cannot exceed 0.1v-0.15v. Therefore, the cross-sectional area of the wire used is relatively large. The high voltage wire of the automobile has a very high withstand voltage, generally should be above 15kv, so its cross-sectional area is small (because the current is small). About 1.5mm2, the thickness of the insulation layer is much lower. Varnished cotton woven bag.
The selection principle of the automobile wire is determined according to the insulation degree of the wire, the current passing through and the required mechanical strength. Electrical equipment that works for a long time can choose wires with an actual carrying capacity of 60%; electrical equipment that works for a short time can choose wires with an actual carrying capacity of 60% to 100%. The automotive electrical system belongs to low-voltage power supply, with large working current and large voltage loss. Excessive voltage loss will affect the normal operation of electrical equipment. Therefore, when conducting wire cross-section and selection, ensure that the voltage loss does not exceed a certain value: 12V system is not greater than 0.5V, 24V system is not greater than 1.0V. The actual working current of the wire is not allowed to be greater than the allowable current carrying capacity of the wire.

 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 简体中文
简体中文 GERMAN
GERMAN SPAIN
SPAIN
 +86 181-5747-1135
+86 181-5747-1135





 Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135
Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135 FAX: +86 574 8900 7636
FAX: +86 574 8900 7636 E-mail:
E-mail: 

 read the map
read the map