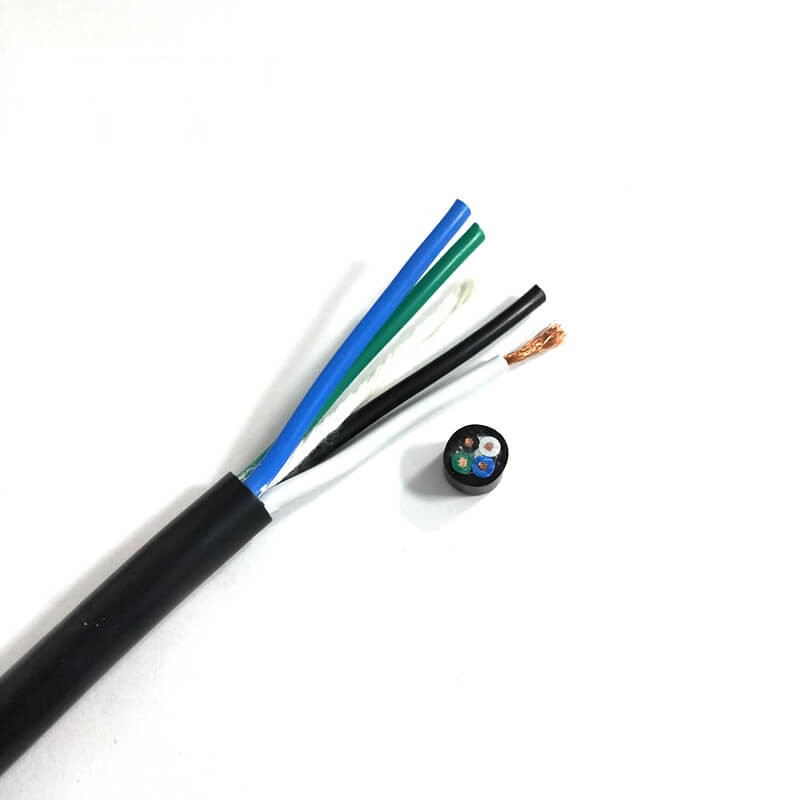
Wire and cable are usually rope-like cables formed by twisting several or several groups of conductors. Each group of conductors is insulated from each other and often twisted around a center. The entire outer surface is covered with a highly insulating covering. Many are erected in the air or installed underground or underwater for telecommunications or power transmission. Cables can be divided into power cables, communication cables and control cables according to their uses. So what are the safety requirements when using wires and cables?
1. When the cables cross each other, the high-voltage cable should be under the low-voltage cable. If one of the cables is protected by a pipe within 1m before and after the intersection or separated by a partition, the minimum allowable distance is 0.25m.
2. When the cable is close to or crossed with the heat pipe, if there are thermal insulation measures, the minimum distances for parallel and cross are 0.5m and 0.25m respectively.
3. When the cable crosses the railway or road, it should be protected by a pipe, and the protection pipe should extend beyond 2m from the track or road surface.
4. The distance between the cable and the foundation of the building should be able to ensure that the cable is buried outside the building water; when the cable is introduced into the building, it should be protected by a pipe, and the protection pipe should also extend beyond the building's water.
5. The distance between the cable directly buried in the ground and the grounding of the general grounding device should be 0.25~0.5m; the buried depth of the cable directly buried in the ground should generally not be less than 0.7m, and should be buried under the frozen soil layer.


 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 简体中文
简体中文 GERMAN
GERMAN SPAIN
SPAIN
 +86 181-5747-1135
+86 181-5747-1135






 Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135
Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135 FAX: +86 574 8900 7636
FAX: +86 574 8900 7636 E-mail:
E-mail: 

 read the map
read the map