The difference between wire and cable depends on the size of the wire is generally small and the structure is relatively simple, but sometimes the cable is also classified as a generalized wire. In a broad sense, it is divided into wires and cables, and in a broad sense, it is generally referred to as a cable. What is the difference between wire and cable? Changyu Cable specializes in the production of various wires and cables. Today, I will answer this question for you.
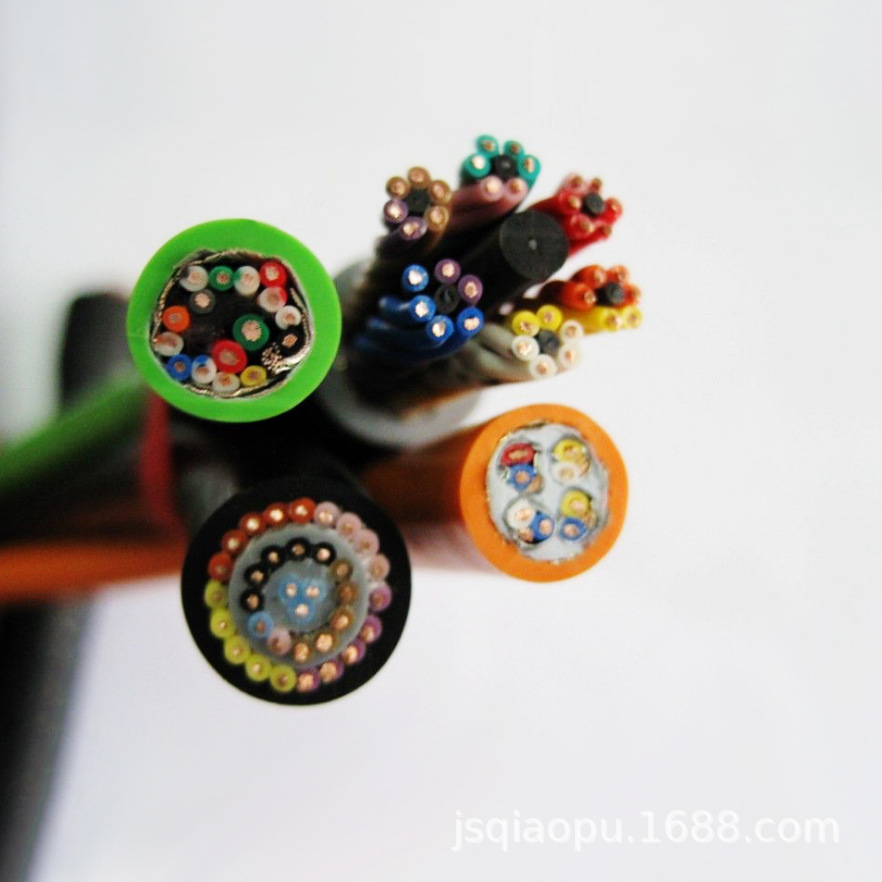
In a broad sense, wires and cables are also commonly referred to as cables. A small range of cables refers to insulated cables, which can be defined as: a combination composed of the following parts; one or more insulated cores, and their respective Cover, total protective layer thickness and outer sheath, the cable may also have additional electrical conductors that are not insulated. Cable enterprise products used to transmit electrical (magnetic) energy, information content and complete electrical energy conversion. Simply put, the wire is composed of one or two soft wires and is covered with a soft outer sheath; the cable is composed of one or two insulated power transmission wires, and the outside is covered with metal materials or rubber. Rubbed hard surface. Cables and wires are generally composed of three components: copper core cable, insulation and outer sheath. Each electrical conductor of a cable can be considered a wire. This is also the most straightforward difference between wire and cable.
1. The difference between raw materials
Conductive carbide molds for electrical wires to carry current. There are various ways such as hollow, stranded or foil woven. According to the insulation situation, it is divided into two categories: bare wire and insulated wire. The cable consists of one or more mutually insulated conductive cores placed in a sealed grommet to produce an insulated transmission line. In addition, maintenance coverage can be added. The difference between wires and cables depends on the specifications of the wires. Generally, they are smaller and simpler in structure, but sometimes cables are classified as generalized wires.
2. The difference in structure
The difference between power engineering cables and general wires is that the cable specifications are relatively large and the structure is more complex. The cable key consists of the following 4 parts. Conductive core: Made of high-conductivity raw materials. Insulation layer: As the insulating material of the cable, it should have high insulation resistance and high penetration field strength. The cable is still insulated.
3. The main purpose of the difference
Bare wires are wires that do not include any insulation or protective covering. In addition to being used as a transmission line for transmitting electromagnetic energy and information, it can also be used to manufacture prefabricated components and electrode connecting lines for electric motors and household appliances. Generally, copper, aluminum, alloy copper and aluminum alloy profiles are used. In addition, there are also a variety of insulated wires that apply special regulations, such as low-voltage wires for automobiles, high-voltage ignition wires for automobiles, lead wires for electric motors and household appliances, airline power lines, thermocouples, etc. Cables are used to transmit, distribute electromagnetic energy or transmit electronic signals. Cables can be divided into power engineering cables, communication cables and manipulation cables according to their application fields.
Apart from the difference inside, the cable still has very obvious advantages. Compared with overhead cables, the advantages of cables are that the insulation distance between wires is small, the floor space is small, the ground is laid without occupying the indoor space above the road, it will not be harmed by the surrounding air pollution, the power distribution stability is high, and it is safe and effective. The surrounding environment has little impact. Therefore, cables are mostly used in densely populated areas and densely populated areas with dense power grids and busy traffic jams. It has an effect that cannot be ignored for modernization.


 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 简体中文
简体中文 GERMAN
GERMAN SPAIN
SPAIN
 +86 181-5747-1135
+86 181-5747-1135






 Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135
Abroad:+86 181 5747 1135 FAX: +86 574 8900 7636
FAX: +86 574 8900 7636 E-mail:
E-mail: 

 read the map
read the map